Suppose you want to enter the sequence \(u_n = \frac{1}{2} + (n-1) \cdot 0.3\) on your calculator.
 and select Add Calculator.
and select Add Calculator.
 , select Actions > Define.
, select Actions > Define.
u(n) =, then write the expression of the sequence.

Suppose you want to enter the sequence \(u_n = 0.3 + u_{n-1}, \text{ with } u_1 = 0.5\) on your calculator.
 and select Add Calculator.
and select Add Calculator.
 , select Actions > Define.
, select Actions > Define.
u(n) =, press  and select.
and select.

Suppose you want to display the graph of the sequence \(u_n = \frac{1}{2} + (n-1) \cdot 0.3\) on your calculator, starting at \(n = 1\) and ending at \(n = 20\).
 and select Add Graphs.
and select Add Graphs.
 , select Graph Entry/Edit > Sequence > Sequence.
, select Graph Entry/Edit > Sequence > Sequence.
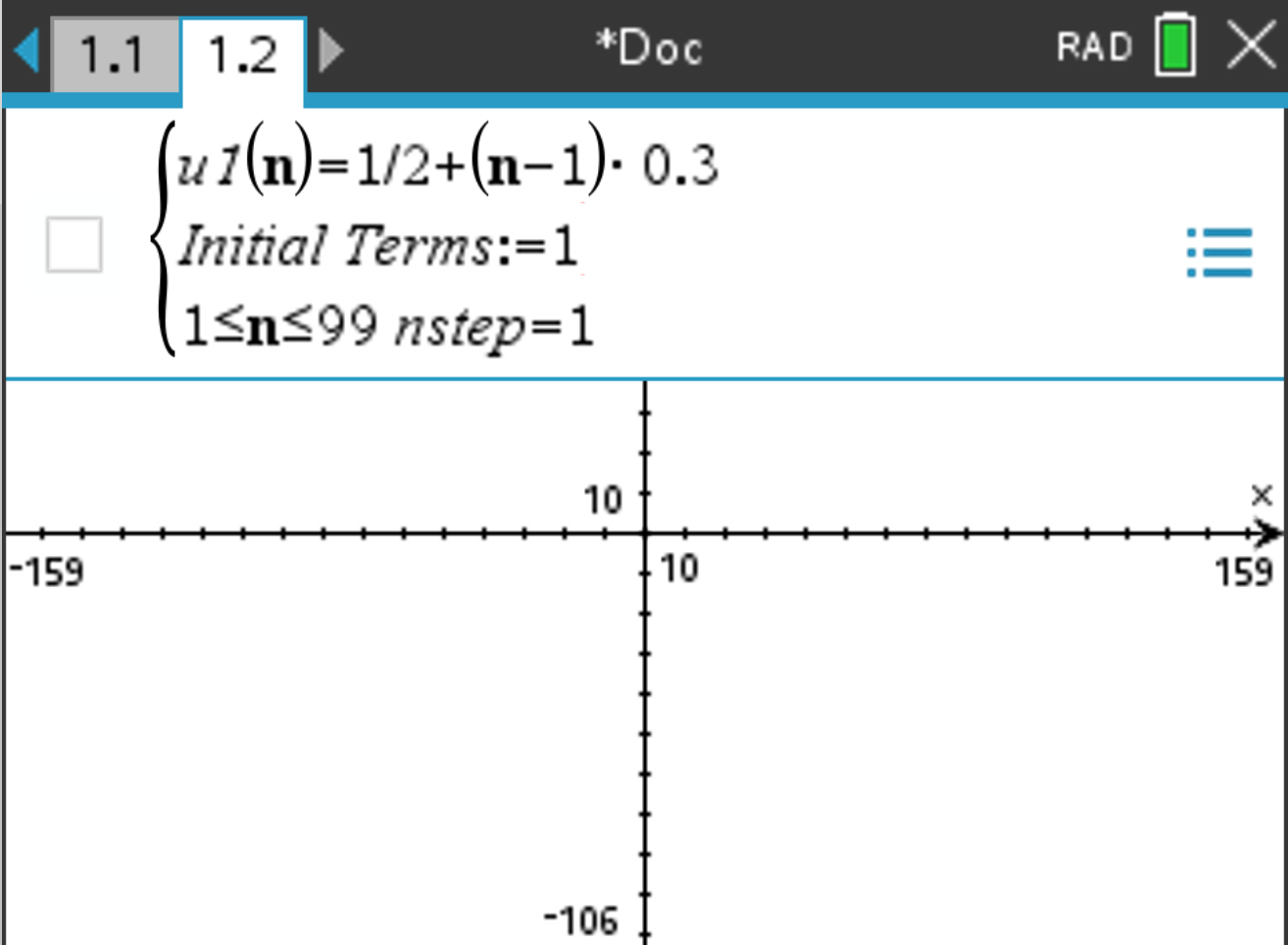
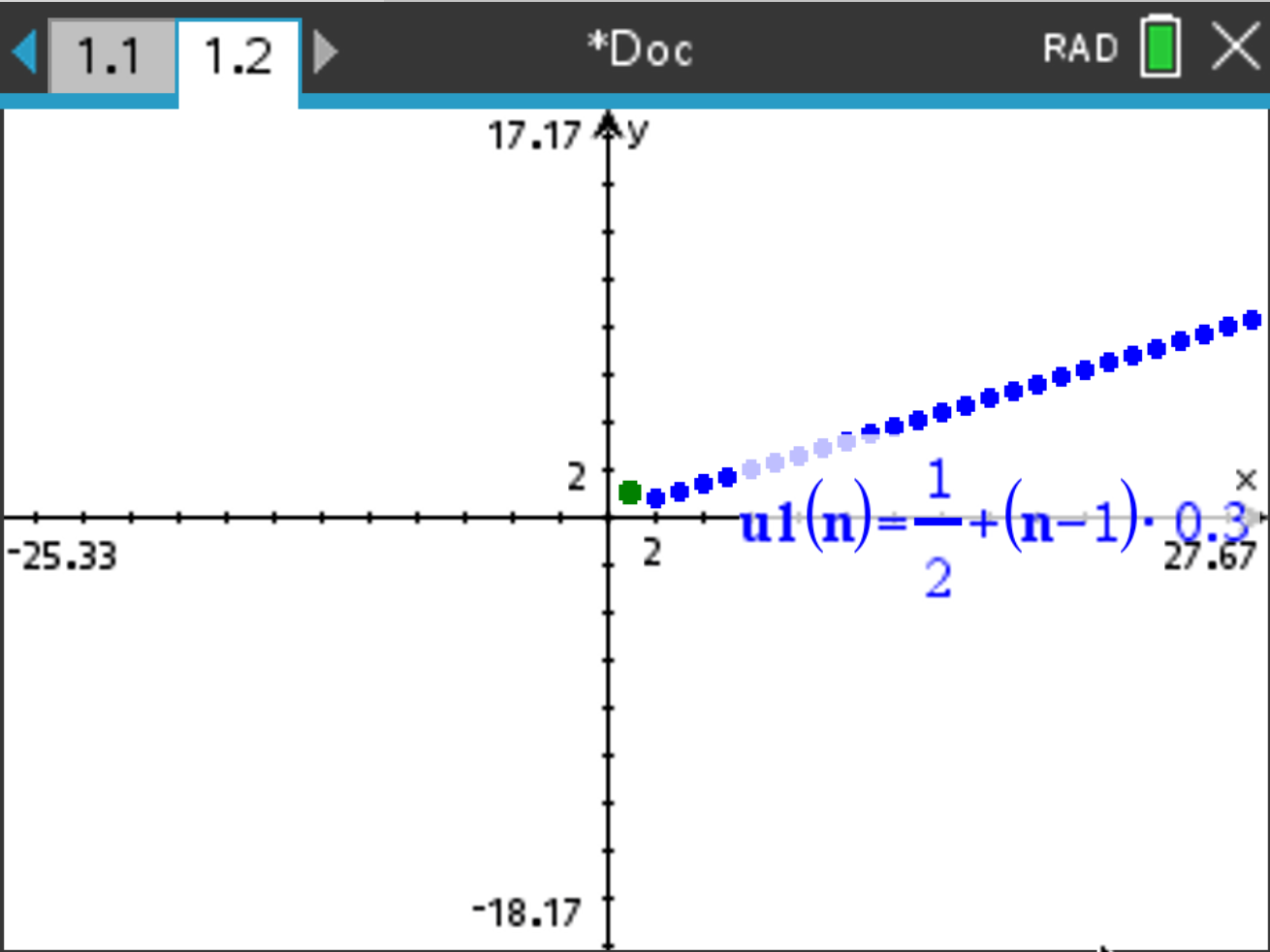
 and the graph of the sequence is displayed.
and the graph of the sequence is displayed.
Suppose you want to know the 320th term of the sequence \(u_n = \frac{1}{2} + (n-1) \cdot 0.3\).
 and write
and write u(320) in the following line.

Suppose you want to graph the series of the sequence \(u(n) = \frac{1}{2} + (n-1) \cdot 0.3\) on your calculator, starting at \(n = 1\) and ending at \(n = 20\).

 and select Add Graphs.
and select Add Graphs.
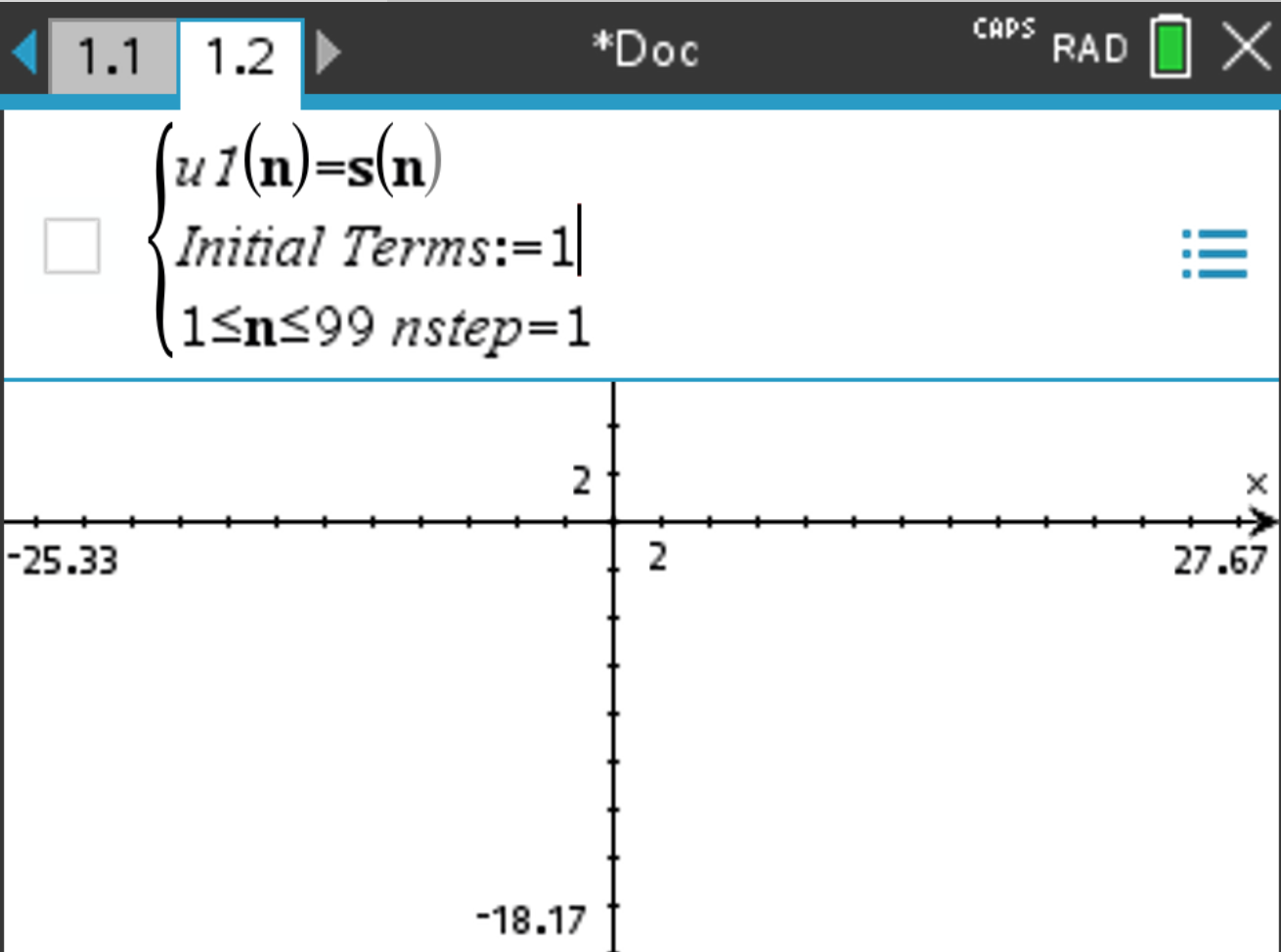
 , select Graph Entry/Edit > Sequence > Sequence.
, select Graph Entry/Edit > Sequence > Sequence.
s(n). In the second line, write the number of initial terms.
 and the graph of the series is displayed.
and the graph of the series is displayed.
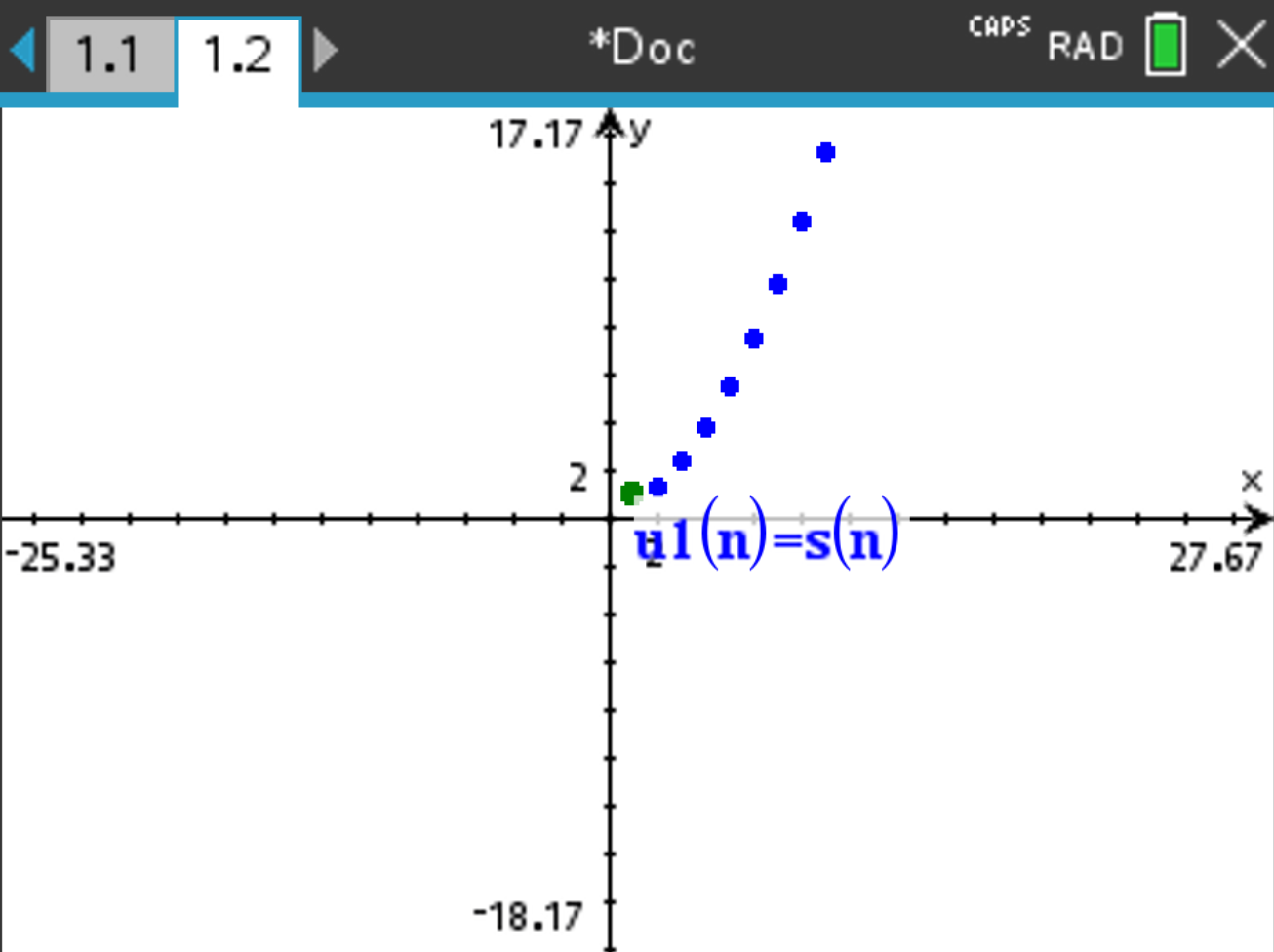
s(20) to set the ending of the series at \(n = 20\). Press  . The result should be \(67\).
. The result should be \(67\).
